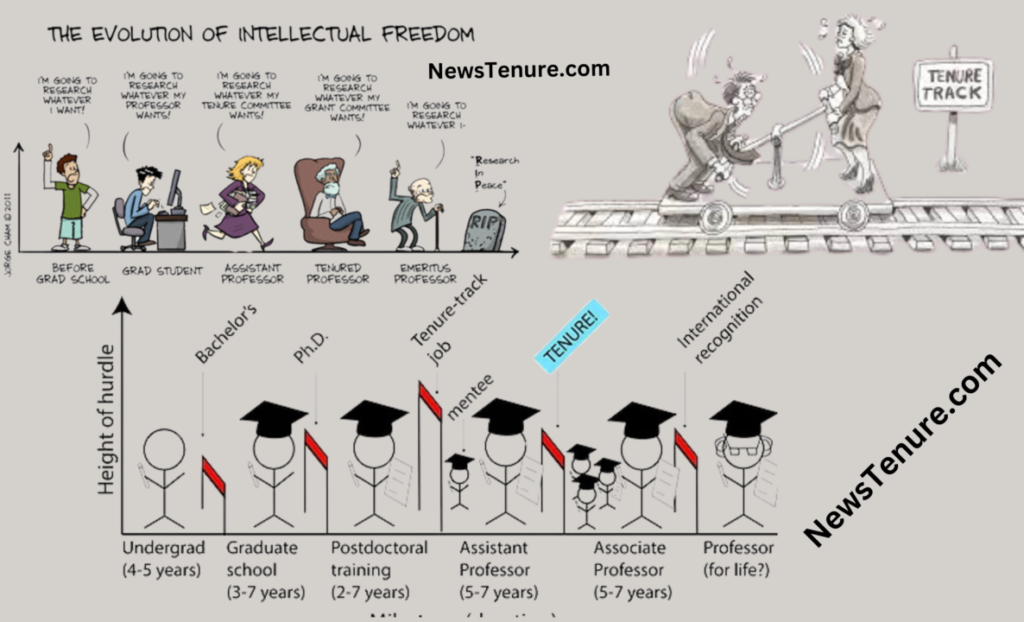
Introduction
Academic tenure is a hallmark of the modern education system, particularly in higher education. It’s a practice that has been both revered and criticized, and its significance in shaping academia cannot be overstated. Tenure is a system designed to protect academic freedom, encourage research, and foster intellectual growth, but it has also been scrutinized for fostering complacency and job security that some claim can hinder the progress and innovation of educational institutions. In this article, we will explore the concept of academic tenure, its history, its benefits, and the controversies surrounding it.
Understanding Academic Tenure
Academic tenure is a contractual arrangement in which a university or college offers a long-term, often indefinite, employment contract to a faculty member. This contract is typically offered to professors, researchers, and sometimes administrators who have demonstrated excellence in their fields. The primary purpose of tenure is to safeguard academic freedom, which is the ability of educators to teach, research, and express their ideas without fear of censorship or retaliation.
The History of Tenure
The concept of academic tenure dates back to the early 20th century, and it has evolved over time. Tenure was introduced to protect educators from arbitrary dismissals and to provide a stable environment for research and scholarship. It was believed that this protection would enable scholars to take risks and engage in innovative and sometimes controversial research without fear of reprisal.
In the United States, higher education has a rich history that dates back to 1636, when Harvard University was established as the country’s first university. But it wasn’t until the 20th century that faculty members were granted tenure as a common benefit.
The American Association of University Professors (AAUP) is an organization tasked with setting guidelines for universities and ensuring that tenure-track faculty members receive the support they deserve. In 1940, the AAUP made the most significant impact when it partnered with the Association of American Colleges and Universities to solidify standards in the Statement of Principles on Academic Freedom and Tenure, even though the organization has been fighting for the rights of educators since its founding in 1915. Over the years, hundreds of colleges and universities have adopted this statement, and a good number of faculty handbooks and collective bargaining agreements include it.
Benefits of Academic Tenure
Protection of Academic Freedom:
Tenure is essential for safeguarding academic freedom, as it ensures that educators can express their opinions, conduct research, and teach without fear of censorship or punishment.
Encouragement of Research:
Tenured professors have the security and stability to pursue long-term research projects that may not yield immediate results, encouraging innovation and the advancement of knowledge.
Quality Education:
Tenure can attract highly qualified and experienced educators who are committed to their disciplines and can provide students with a high-quality education.
Institutional Memory:
Tenured faculty often provide continuity and institutional memory, helping maintain the standards and values of the educational institution over time.
Controversies Surrounding Tenure
Lack of Accountability:
Critics argue that tenure can lead to complacency and a lack of accountability among faculty members, as they are guaranteed employment regardless of their performance.
Difficulty in Removing Underperforming Faculty:
Tenure can make it challenging for universities to remove faculty members who may no longer be effective or engaged in their roles.
Limited Opportunities for Younger Scholars:
The prevalence of tenured positions can limit opportunities for young scholars and researchers who face stiff competition for a limited number of tenure-track positions.
Financial Concerns:
Critics also point out that the cost of tenured positions can strain university budgets, potentially leading to higher tuition fees and a focus on research at the expense of teaching.
Recent Developments in Tenure
In recent years, some universities have been exploring alternative models to traditional tenure, such as long-term contracts, post-tenure review processes, and non-tenure track positions. These changes are intended to address concerns about accountability, financial sustainability, and equity in hiring practices.
Conclusion
Academic tenure remains a pivotal component of higher education, intended to protect academic freedom and promote research and innovation. However, it has not been without its share of controversies and criticisms. As the landscape of higher education continues to evolve, institutions must strike a balance between maintaining the core principles of academic tenure. Addressing the legitimate concerns raised by its critics. The future of tenure may involve adapting its traditional model to better serve the needs of both educators and students in a rapidly changing academic environment.