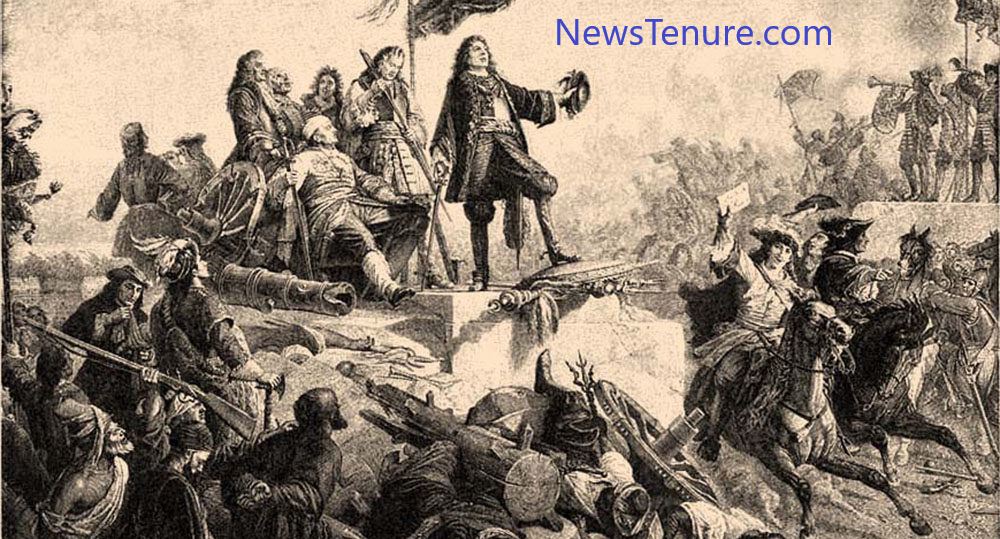
The Ottoman Empire, one of history’s most influential and expansive empires, continues to captivate the imagination of people around the world. Today, in our exploration of world history, we delve into the rich heritage of the Ottoman Empire. This article, brought to you by News Tenure, aims to provide a glimpse into the history, accomplishments, and lasting impact of this remarkable empire.
Origins and Expansion:
The Ottoman Empire, founded by Osman. In the early 14th century, emerged as a small Anatolian principality in what is now modern-day Turkey. Over the centuries, the empire expanded through a combination of military conquests, strategic alliances, and skilled diplomacy. Its central location facilitated connections between Europe, Asia, and Africa. That making it a vital player in the geopolitics of the time.
The Golden Age Ottoman Empire
Under the reign of Sultans Mehmed the Conqueror, Suleiman the Magnificent, and their successors, the Ottoman Empire experienced its golden age. It became a dominant force in the Mediterranean and the Middle East, extending its influence across vast territories. The empire’s capital, Istanbul (formerly Constantinople), flourished as a cosmopolitan center of trade, culture, and intellectual exchange.
Innovations and Cultural Contributions:
The Ottoman Empire fostered an environment conducive to artistic, scientific, and intellectual advancements. The empire’s architects created breathtaking mosques, palaces, and public buildings, characterized by intricate design and grandeur. The Empire’s scholars and thinkers made significant contributions to fields such as mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and literature, leaving an enduring impact on Islamic civilization.
Legal System and Governance:
The Ottoman Empire developed a comprehensive legal system based on Islamic law, known as Sharia, combined with local customs and regulations. The empire’s governance structure, led by the Sultan and supported by a bureaucracy of officials, aimed to maintain stability and administer justice. The millet system, which granted religious autonomy to various communities, allowed for cultural diversity within the empire.
Trade and Economic Prosperity:
Trade played a vital role in the Ottoman Empire’s prosperity. It controlled key trade routes, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies between Europe, Asia, and Africa. Istanbul, with its strategic location along the Silk Road and maritime routes, emerged as a bustling commercial hub. The empire’s economic success enabled the development of infrastructure, including road networks, bridges, and public buildings.
Decline and Legacy:
The Ottoman Empire’s decline began in the late 17th century, marked by military setbacks, internal strife, and challenges from emerging European powers. It faced territorial losses and increasing pressures from nationalist movements within its diverse population. By the early 20th century, the empire transformed into the modern nation-state of Turkey after a series of reforms led by Mustafa Kemal Atatürk.
Nevertheless, the Ottoman Empire’s legacy endures to this day. Its impact on art, architecture, and cultural practices can be seen in numerous historical sites and traditions. Additionally, its governance model and legal principles continue to influence the legal systems of many countries with an Islamic heritage.
Conclusion:
The Ottoman Empire stands as a testament to the power, resilience, and cultural achievements of a once-great civilization. Its contributions to the realms of art, science, and governance have left an indelible mark on history. As we reflect on the past, we recognize the importance of understanding and appreciating the diverse legacies that have shaped our world today.